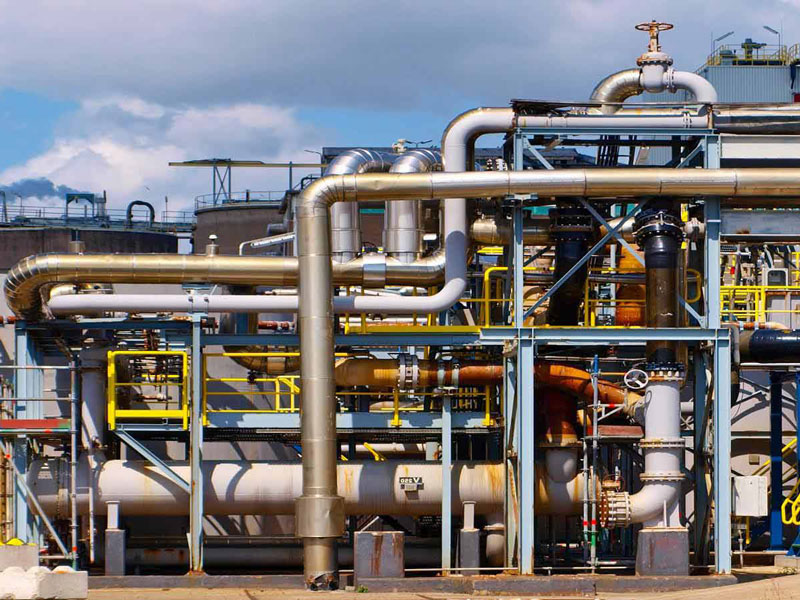
Advance Pipe Stress Engineering Course in Mumbai equips engineers with the critical knowledge needed to design safe, efficient, and code-compliant piping systems. To create an effective design, engineers must analyze the system’s behavior under various mechanical and thermal loads. This includes assessing stress, pressure, temperature effects, and determining optimal support placement to ensure structural integrity and smooth operation.
Understanding and applying industry standards like ASME, ANSI, and API is crucial for legal, environmental, and safety compliance. A properly engineered piping system should strike a balance between performance, safety, and long-term reliability. The Advance Pipe Stress Engineering Course in Mumbai focuses on global best practices and prepares professionals to meet complex industry demands with confidence.
Field Scope & Importance
- Engineers must adhere to industry standards like ASME, ANSI, and API for safety and reliability.
- Understanding thermal, pressure, and mechanical loads is crucial for system integrity.
- Proper stress analysis ensures the piping system can withstand operational conditions.
- Choosing the right materials is key to durability and compatibility with fluids.
- Efficient piping layout minimizes pressure drops, reduces cost, and improves accessibility.
- Well-designed systems prevent leaks, failures, and hazards in industrial environments.
Eligibility
- Diploma/Degree (chemical/mechanical) with Piping Knowledge
Working Steps for Advance Pipe Stress Engineering

System Modeling
Create a 3D model of the piping network with accurate material, geometry, and support data. This forms the foundation for stress and flexibility analysis.

Load Definition
Apply thermal, pressure, seismic, and weight loads to simulate real-world operating conditions. Proper load cases ensure compliance with safety standards.

Stress Analysis
Evaluate pipe behavior under various loads using tools like CAESAR II. Identify overstressed areas and modify the design accordingly.

Compliance Check
Check results against design codes like ASME B31.3 and generate reports. Ensure the system is safe, reliable, and documentation-ready.
Curriculum
- Introduction to Pipe Stress Analysis
- Stress Categories
- Pipe Support Span Calculations
- Standard Compliance for various equipments
- Piping Configuration
- Miscellaneous
- Defining Load Cases
- Code Compliance: Stresses –Sustained, Expansion,Operating, Occasional
- Typical Piping Configuration for ease in analysis
Core Functions of a Advanced Pipe Stress Engineering
Stress Analysis
Evaluates the impact of thermal, pressure, and mechanical loads on piping systems.
Code Compliance
Ensures piping designs meet global industry standards like ASME and ANSI.

Material Selection
Assesses materials resistance to stress, corrosion, & temperature extremes.
System Optimization
Identifies stress points to optimize design and reduce risks of failure.

Simulation Tools
Uses advanced software like CAESAR II and ANSYS for precise stress modeling.

Safety Assurance
Focuses on preventing failure, leaks, and damage in critical piping systems.
An Advance Pipe Stress Engineering Course in Mumbai at Trinkets Institute of Technology (TIT) equips you with the skills to analyze and optimize piping systems using industry-leading tools like CAESAR II. Mumbai, India’s epicenter for oil, gas, and petrochemical industries, is the ideal location for an Advance Pipe Stress Engineering Course in Mumbai. This article explores why TIT’s course is a career-transforming opportunity, what you’ll learn, and how it prepares you for high-demand roles in engineering.
Why Choose an Advance Pipe Stress Engineering Course in Mumbai?
Ensuring Piping System Integrity
Pipe stress engineering is critical for designing safe, reliable piping systems that withstand thermal, pressure, and dynamic loads in industries like refineries and power plants. Mumbai’s industrial giants, such as Reliance Industries, ONGC, and L&T Hydrocarbon, rely on skilled pipe stress engineers to ensure system reliability. TIT’s Advance Pipe Stress Engineering Course in Mumbai trains you to perform stress analysis, optimize designs, and ensure compliance with global standards, positioning you as a top talent in EPC firms.
Mumbai’s Industrial Hub
Mumbai’s proximity to refineries, chemical plants, and mega-projects makes it the perfect place for an Advance Pipe Stress Engineering Course in Mumbai. TIT’s Mulund campus immerses you in this dynamic ecosystem, offering hands-on exposure and access to thriving job markets. From petrochemical expansions to energy projects, Mumbai provides an unparalleled platform for career growth.
What You’ll Learn in TIT’s Advance Pipe Stress Engineering Course
Comprehensive Curriculum
TIT’s Advance Pipe Stress Engineering Course in Mumbai delivers a focused curriculum over 1-3 months, with flexible weekday, weekend, or online batches. Designed for both beginners and professionals, the course covers:
Piping Stress Analysis: Master CAESAR II for thermal, pressure, and seismic load analysis.
Code Compliance: Ensure designs meet ASME B31.3, API, and EN standards.
Support Design: Optimize pipe supports and hangers for stability and cost efficiency.
Dynamic Analysis: Analyze vibration, wind, and transient loads for system reliability.
Integration with Design Tools: Coordinate with piping and structural design software.
Through hands-on projects, like analyzing a refinery piping system, you’ll gain practical expertise. The course aligns with TIT’s AutoCAD Course in Mumbai, enabling you to create precise 2D and 3D piping layouts to complement your stress analysis skills.
Industry-Focused Training
With small batches of 7-10 students, TIT ensures personalized instruction from expert instructors. You’ll tackle real-world challenges, such as optimizing a high-pressure piping system, preparing you to meet industry standards with precision. Exposure to tools like AutoPIPE and PDMS ensures you’re ready for integrated design workflows.
Why TIT is the Premier Choice
Expert Faculty and Certification
Since 2011, TIT has been ISO 9001:2015 certified, delivering industry-aligned training. Our Advance Pipe Stress Engineering Course in Mumbai is led by professionals with extensive experience in piping design and analysis. You’ll earn globally recognized certificates, valued by employers like TechnipFMC and Jacobs Engineering, boosting your professional credibility.
Affordable Fees and Proven Placements
TIT offers competitive fees, ensuring accessibility for all. Our placement cell boasts an 80% success rate, with alumni like Shubham Patil (Tata Consulting Engineers, 6 lakhs/year) and Mahesh Gosavi (Tata Consulting Engineers, 7.2 lakhs/year) securing top roles. TIT provides resume-building workshops, mock interviews, and direct connections to industry recruiters.
Career Opportunities After the Course
An Advance Pipe Stress Engineering Course in Mumbai unlocks roles like pipe stress engineer, piping designer, or plant engineer. Starting salaries range from 4-6 lakhs annually, with experienced professionals earning 10 lakhs or more. Mumbai’s industrial sector, driven by projects like refinery upgrades and green energy initiatives, ensures strong demand for pipe stress expertise.
Why Choose TIT in Mumbai?
TIT’s Advance Pipe Stress Engineering Course in Mumbai is a career accelerator, combining practical training, expert mentorship, and robust placement support. Located in Mulund, with online options, TIT offers flexibility to suit your lifestyle.
Take the Leap Today
Don’t wait to shape your future. An Advance Pipe Stress Engineering Course in Mumbai at TIT empowers you to design safe, efficient piping systems for global industries. Enroll now to master pipe stress engineering and launch a rewarding career in Mumbai’s thriving industrial landscape.


